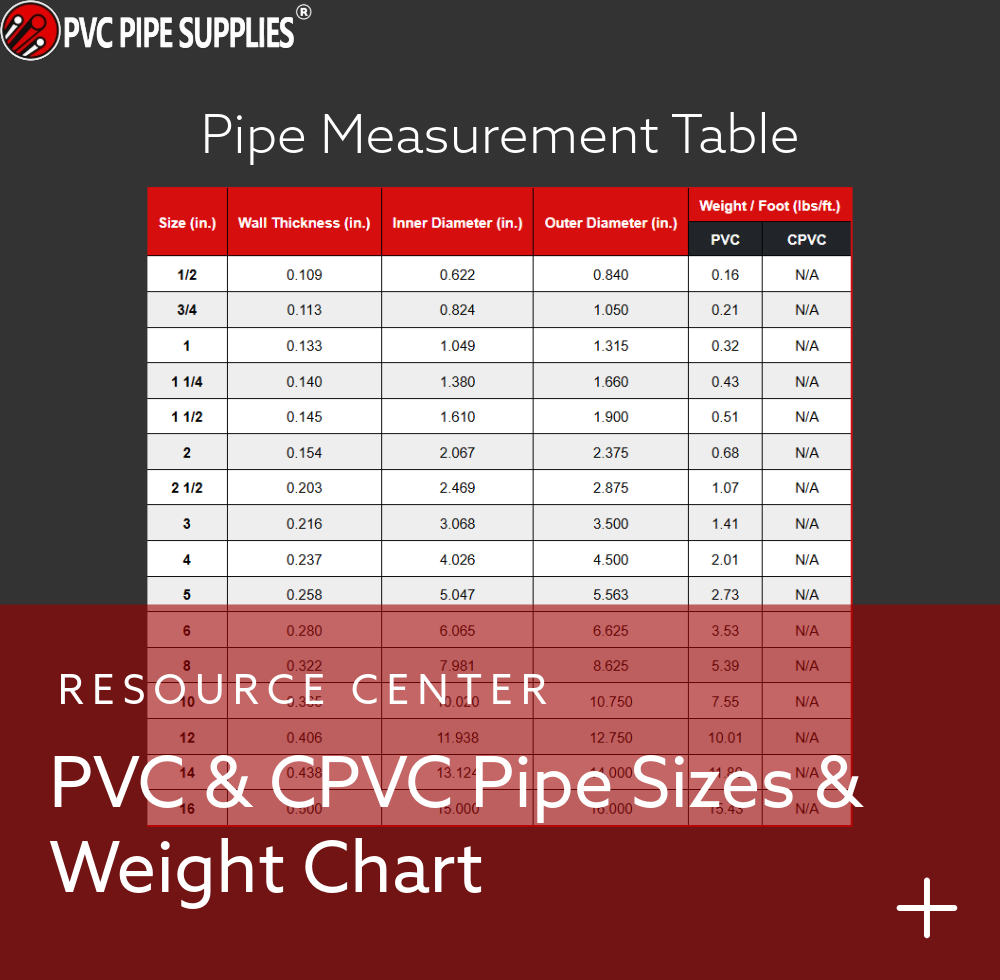
When selecting materials for plumbing and piping systems, the options can seem overwhelming. One standout solution is CPVC pipe, trusted for its professional versatility and reliable performance. But what exactly is CPVC, and why is it a possible solution for modern plumbing applications?
CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) is a thermoplastic material based on raw PVC that has undergone further chlorination, which in turn improves its chemical resistance, durability, and temperature tolerance. Unlike standard PVC, which is primarily used for cold water systems, CPVC can handle hot and cold water as well as many chemicals. This makes it suitable for a variety of residential, commercial, and industrial purposes. CPVC blends corrosion, scaling, and chemical degradation resistance to offer a premium combination of reliability and longevity that sets the material apart.
Over the years, CPVC pipe has become a valuable component in modern plumbing and piping systems. Its versatility lends itself to a range of applications, from carrying potable water in homes and transporting high purity ingredients to handling fumes and heated chemicals in industrial facilities. The increased adoption of CPVC across industries is a testament to its reliability, with statistics showing a steady rise in its usage worldwide.


Key Properties of CPVC
Durability and Chemical Resistance
CPVC pipe has been specifically engineered with excellent physical strength and chemical resistance to handle the demands of modern plumbing systems and deliver professional performance across a variety of working conditions.
A major factor contributing to CPVC's value and versatility is its chemical durability. Due to the chlorination process, CPVC is compatible with a broad range of chemicals, including acids, bases, salts, inorganic compounds, and various organics. This makes it particularly ideal for industrial settings that handle corrosive or reactive substances. Whether used in chemical processing facilities or residential plumbing systems, the overall strength of premium quality CPVC pipe ensures long term, trouble free performance.
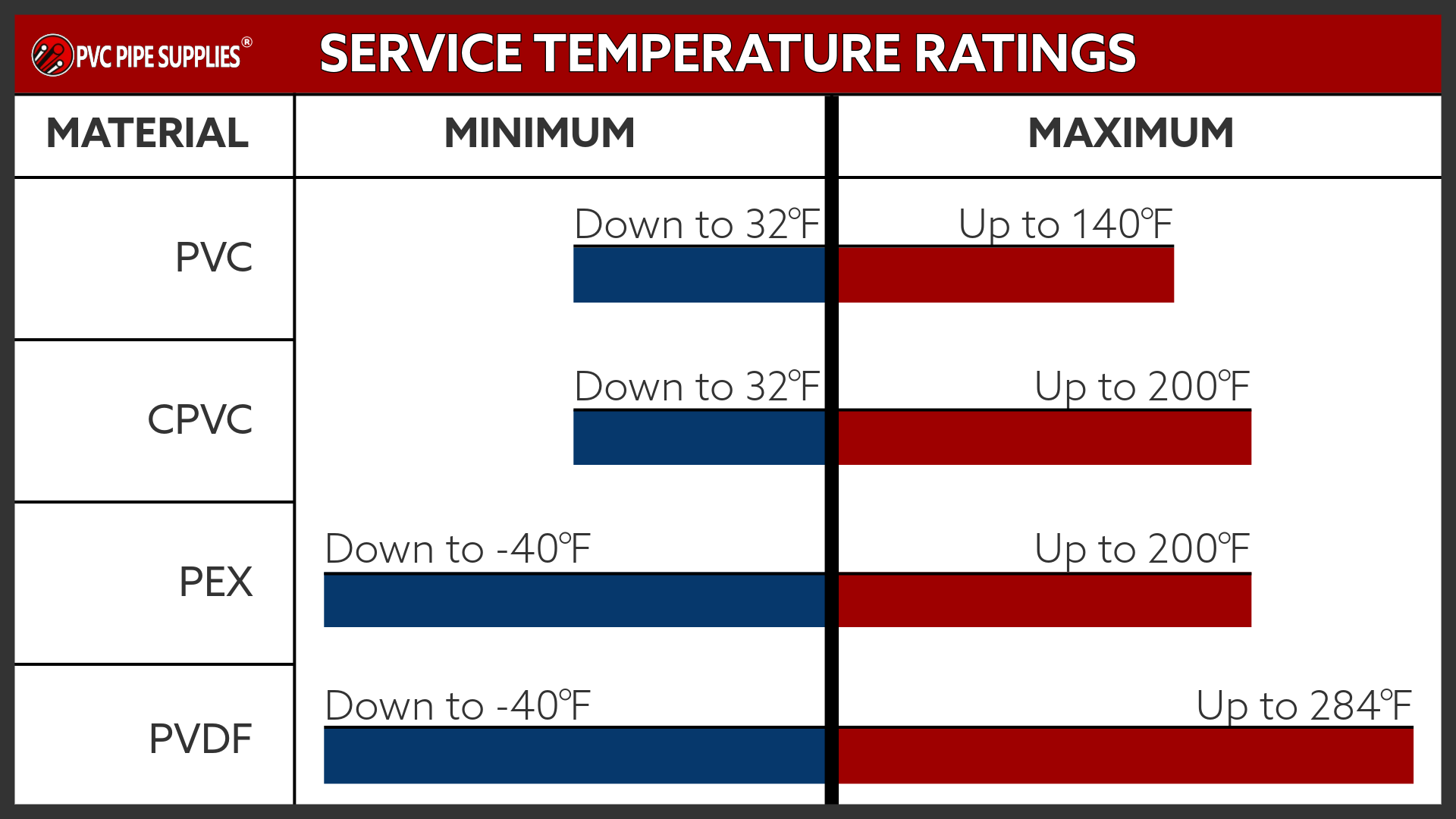

Temperature Tolerances
Unlike materials prone to damage from thermal expansion, CPVC maintains its structural integrity even when exposed to fluctuating temperatures. This characteristic ensures durability for both hot and cold pipelines while reducing long term maintenance needs and minimizing the risk of failures.
CPVC pipe’s ability to withstand high temperatures is one of the key attributes that distinguishes it from standard PVC. While PVC is only suitable for cold water systems, CPVC can operate safely under hotter conditions.
The safe operating temperature range for Schedule 80 CPVC pipe generally falls between 33°F and 200°F — the low range is based on the freezing point of water. This makes it acceptable for a variety of heated applications, including residential hot water lines and industrial processes. For comparison, standard PVC has a lower temperature tolerance, with a maximum temperature around 140°F, which restricts its uses. Other materials, such as metal pipes, can handle even higher temperatures but lack CPVC's lightweight structure, lasting corrosion resistance, and cost savings.
Longevity and Safety
With quality products, proper installation and maintenance, CPVC systems have an impressive lifespan potential. With many installations lasting 50 years or more, CPVC has proven itself as a durable material that can withstand the passing of time and repetitive use. This longevity makes CPVC plumbing an excellent investment as well as a cost effective one as the need for repairs or replacements is minimized.
Safety is another factor that adds to the value of CPVC. Professional grade CPVC pipe is manufactured from Type IV cell class 23447 resin, premium Corzan CPVC material. Piping is tested post-production to ensure compliance with applicable ASTM performance and safety standards to ensure it meets the proper specifications for overall strength, thickness, and pressure tolerance.
Many CPVC pipes and fittings are also NSF certified, which verifies that the material meets strict health and safety standards for potable water use. CPVC is a chemically inert material that does not leach harmful substances into the water supply. This makes CPVC a trustworthy choice in the water delivery systems of households, commercial buildings, and industries.
Review on CPVC Pipe Properties
With its superior durability, excellent temperature range, and remarkable safety profile, CPVC has earned its place as a reliable option in plumbing and piping applications. These properties not only make it a versatile choice but also provide contractors, industry professionals, and DIYers with the confidence needed to trust CPVC pipe for their projects.
Common Applications of CPVC Pipes
Residential Plumbing
CPVC pipes have become a practical and reliable choice for residential plumbing as an alternative to traditional options such as copper. Whether you're installing water supply lines for a single family home or outfitting a multi unit building, CPVC can be trusted to deliver consistent, long lasting service.
One significant advantage of CPVC in residential plumbing is its natural resistance to scaling and corrosion, which is a common concern with materials like copper, especially in well water or hard water systems.
Unlike metal pipes, CPVC is not susceptible to pitting or rust, even in water with high mineral content. This durability translates into fewer maintenance issues and a longer service life in the long run.
CPVC pipes are also lightweight and easy to install, in turn saving labor time and costs. They can be cut, shaped, and joined quickly and easily, making them ideal for DIY projects or fast tracked professional installations. Given its price compared to copper and its high performance, CPVC makes an overall excellent solution for modern residential construction projects.


Industrial Applications

CPVC has a wide range of industrial uses due to its heavy duty chemical resistance and high temperature tolerance. One of its primary applications in the industrial sector is in chemical processing plants where CPVC is used to transport corrosive chemicals, including acids, bases, and other reactive substances.
Its ability to withstand chemical exposure without rapid degradation makes it an ideal choice for plumbing networks, fume scrubbers, and ductwork systems where safety and reliability are top priorities.
Another frequent industrial application for CPVC is in water treatment and processing facilities. Industrial water treatment often involves activities like filtration, separation, chemical dosing, and wastewater management, all of which require materials capable of withstanding the conditions. CPVC's resistance makes it ideal for transporting byproducts or water with chemical additives, such as chlorine, which can corrode other materials. CPVC's lightweight design and easy installation make it a preferred choice in large scale industrial setups.
Niche or Emerging Applications
While CPVC is well established in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, its adaptability has led to niche and emerging applications in specialized fields.
For example, CPVC is increasingly being used in healthcare facilities and laboratories to transport pure water, critical-process fluids, and lab waste. The material's chemical inertness and NSF certification for potable water further ensure its suitability for these sensitive applications. Special formulations of CPVC pipe, such as Spears Labwaste CPVC Pipe and Spears PVC Low Extractable Pipe, have been specifically engineered for such applications.
Another emerging use of CPVC is in photovoltaic solar panel systems, where it serves as a conduit for coolants or protective piping for electrical wires or components. The material's ability to endure high temperatures and exposure to UV radiation improves its performance in outdoor and energy applications.
From homes to industrial plants and modern facilities, CPVC's versatile set of applications demonstrates its reliability, adaptability, and growing importance. Whether you're looking to complete residential installations or meet industrial demands, CPVC continues to prove why it’s a standout option in plumbing and piping solutions.


Addressing CPVC Concerns: Quality Matters
When selecting CPVC pipes for your plumbing or industrial projects, information found some places online may express concerns about brittleness, reduced lifespan, and overall reliability. These issues associated with CPVC are often the result of improper installation, exposure to incompatible chemicals, or the use of low quality products, a primary culprit. At PVC Pipe Supplies, we prioritize only top quality products made by trusted USA manufacturers to ensure these concerns never impact your plumbing systems.
For a deeper look into this, read Common Myths About CPVC Pipes: The Facts.
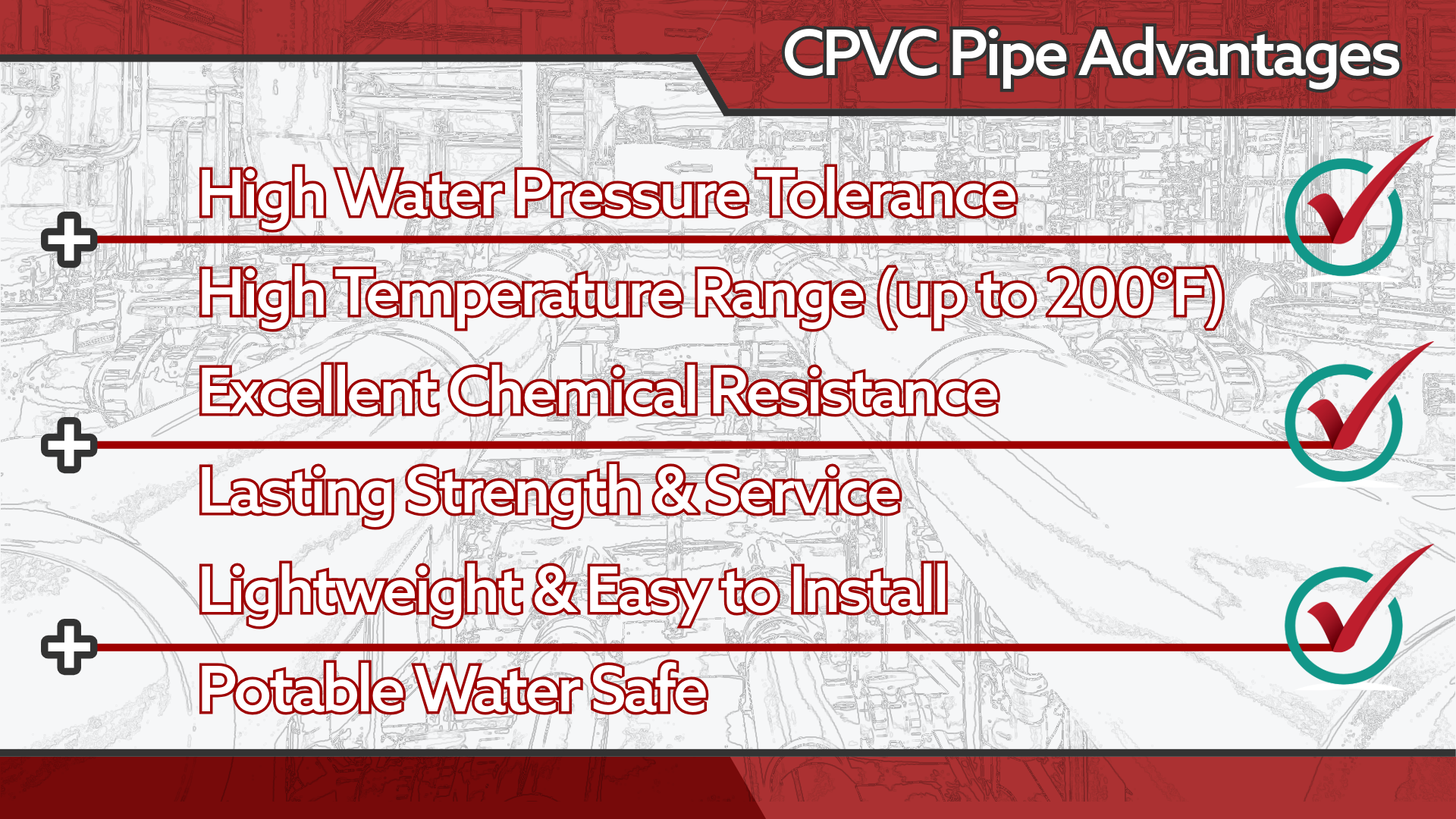

Advantages of CPVC Pipe
Comparing Costs to Copper or Steel
One of the most compelling benefits of CPVC pipe is its cost effectiveness. Compared to traditional materials like copper or steel, CPVC offers significant savings without compromising on performance. Copper, for instance, is not only expensive to purchase but also requires skilled labor and special tools for installation that increase overall project costs. Similarly, steel pipes can be costly due to their material price and the additional maintenance required to prevent corrosion and rust.
CPVC pipes, on the other hand, are often much more affordable to buy and install. They are lightweight, which reduces shipping costs and makes for easy handling, and their straightforward installation process leads to lower labor expenses. Whether you're a contractor outfitting a commercial building or a plant manager, CPVC pipe ensures you get high quality results at a fraction of the price of metal alternatives.
Resists Corrosion and Reduces Contamination Risks
CPVC pipe has excellent corrosion resistance. Unlike copper and steel, which can degrade over time when exposed to moisture, outdoor environments, or aggressive chemicals, CPVC remains unaffected by these concerns. Its chlorinated polymeric structure makes it highly resistant to both rust and scaling, even in hard water applications. This resilience will keep CPVC systems performing consistently with minimal maintenance.
CPVC's inert nature, (meaning non-reactive with water), significantly reduces the risk of harmful substances leaching into water supplies. This is especially important for freshwater handling as the water delivered to homes, businesses, and industrial sites must be safe and free of contaminants.
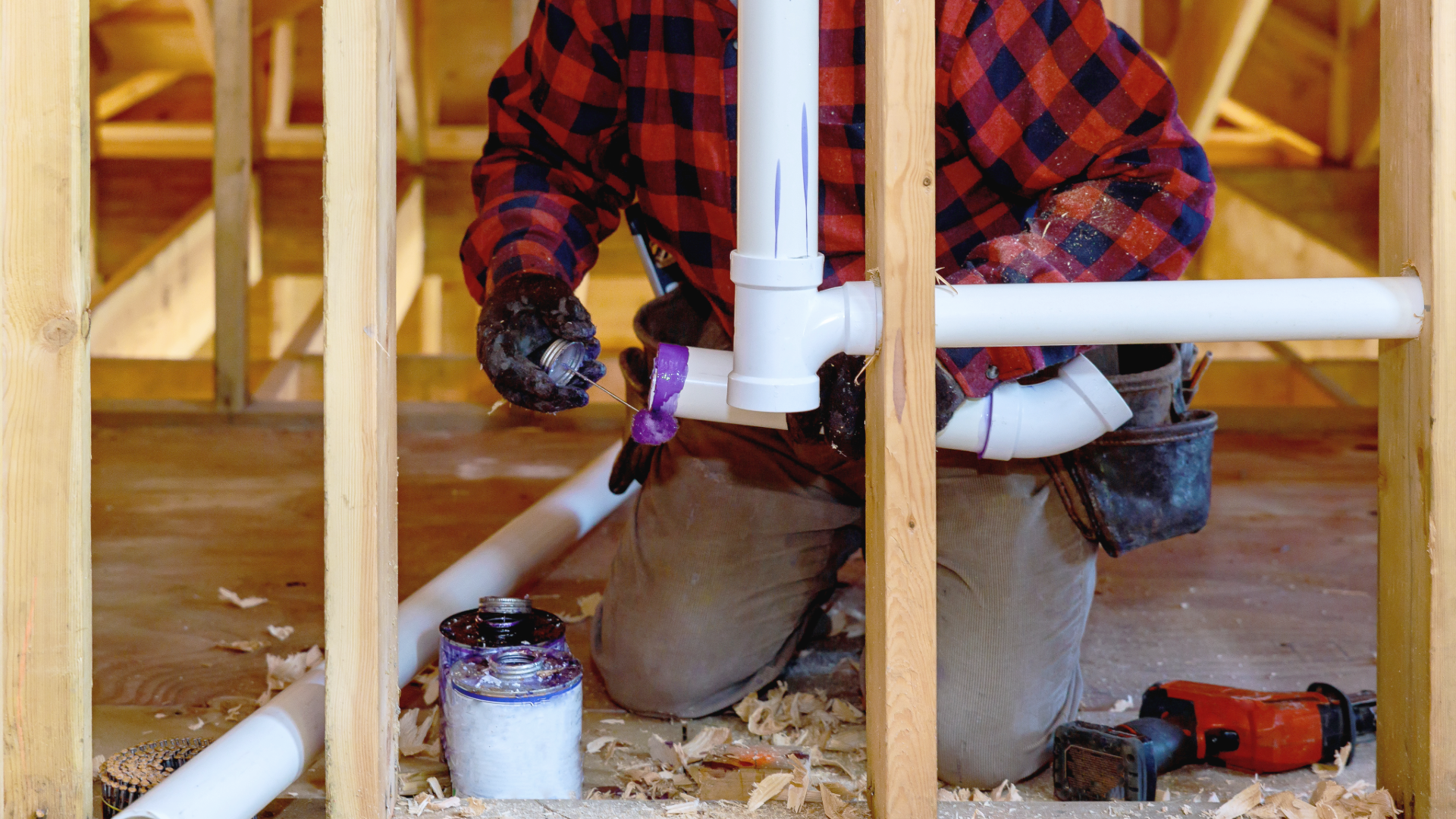




Easy Installation
Installing CPVC plumbing is simple and straightforward, making it a popular choice for contractors and DIYers alike. A primary reason for this is due to the solvent welding process. Solvent welding allows pipes and fittings to bond chemically, effectively creating a single piece for a strong and leak resistant connection. Unlike metal pipes, which often require threading, soldering, or welding, CPVC installations can be completed with basic tools, the right pipe cement and primer, and minimal training.
The lightweight nature of CPVC also simplifies the process as it is easy to transport, handle, and cut to the desired length. This contrasts sharply with materials like steel, which are heavy and cumbersome, or copper, which requires cutting and soldering expertise. By reducing the complexity of installation, CPVC pipe not only saves time but also minimizes the likelihood of errors.
Installation Tips for CPVC Pipe
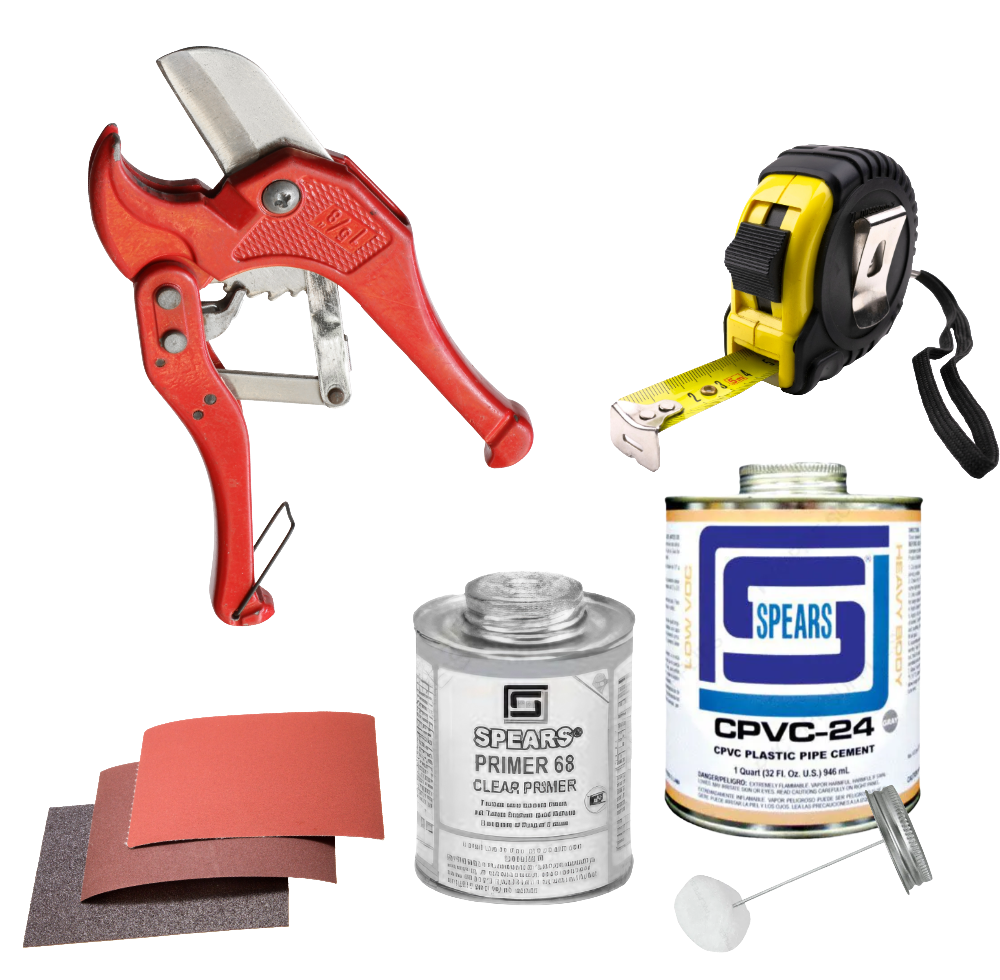
Tools and Materials Required
Before starting your CPVC pipe installation, have the right tools and materials on hand. This will ensure a smooth process and help achieve long lasting, leakproof connections. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Solvent Cement and Primer: The solvent cement chemically bonds CPVC components to create a secure and watertight seal. The primer is used to clean and prepare the surfaces of fittings and pipes for optimal adhesion. Always make sure to use the correct primer and cement for the pipe and the job.
- Cutting Tools: Use a specialized PVC / CPVC pipe cutter, ratchet cutter, or even a handsaw to cut the pipe cleanly. Precision is key to avoid jagged edges that could compromise the connection.
- Measuring Tools: A measuring tape offers accuracy while marking the pipe for cuts. Accuracy in these measurements prevents gaps or overlap during the installation.
- Deburring Tool or Sandpaper: To smooth rough edges after cutting, use a deburring tool or fine grit sandpaper. Eliminating burrs will help ensure pipes fit snugly into fittings and reduce the risk of leaks.
Having these items ready will save time and prevent project hang-ups.


Step-by-Step Guide to Proper Installation
Follow these steps to ensure a successful CPVC pipe installation:
- Cut the Pipe: Measure and mark the CPVC pipe at the desired length. Use a cutter or saw to make a clean, straight cut. Smooth the edges with a deburring tool or sandpaper to eliminate roughness.
- Dry Fit the Connections: Before applying primer or cement, dry-fit the pipe and fittings to ensure they align correctly. Mark orientation points if necessary for proper alignment after bonding.
- Prepare the Surfaces: Use a CPVC primer to clean and prep the outside of the pipe and the inside of the joining pipe or fitting. The primer softens the material slightly, allowing better adhesion. Allow it to dry for a moment before proceeding.
- Apply the Cement: Use a solvent cement specifically designed for CPVC pipes. Apply a thin, even layer to both the pipe end and the fitting socket. Work quickly but carefully, as the cement sets fast.
- Join the Components: Push the pipe into the fitting with a twisting motion until it seats fully in the socket. Hold it in place for 10-15 seconds to ensure a strong initial bond.
- Wipe Away Excess Cement: Use a cloth to clean up any excess solvent cement that squeezes out during the connection process. This prevents unsightly marks and ensures the bond remains clean.
- Allow for Cure Time: Consult the solvent cement instructions for cure times, as they can vary depending on temperature and humidity. Avoid applying pressure or testing the system until the recommended curing period has passed.
- Test the System: Once cured, test the system to ensure all connections are secure and leak free.
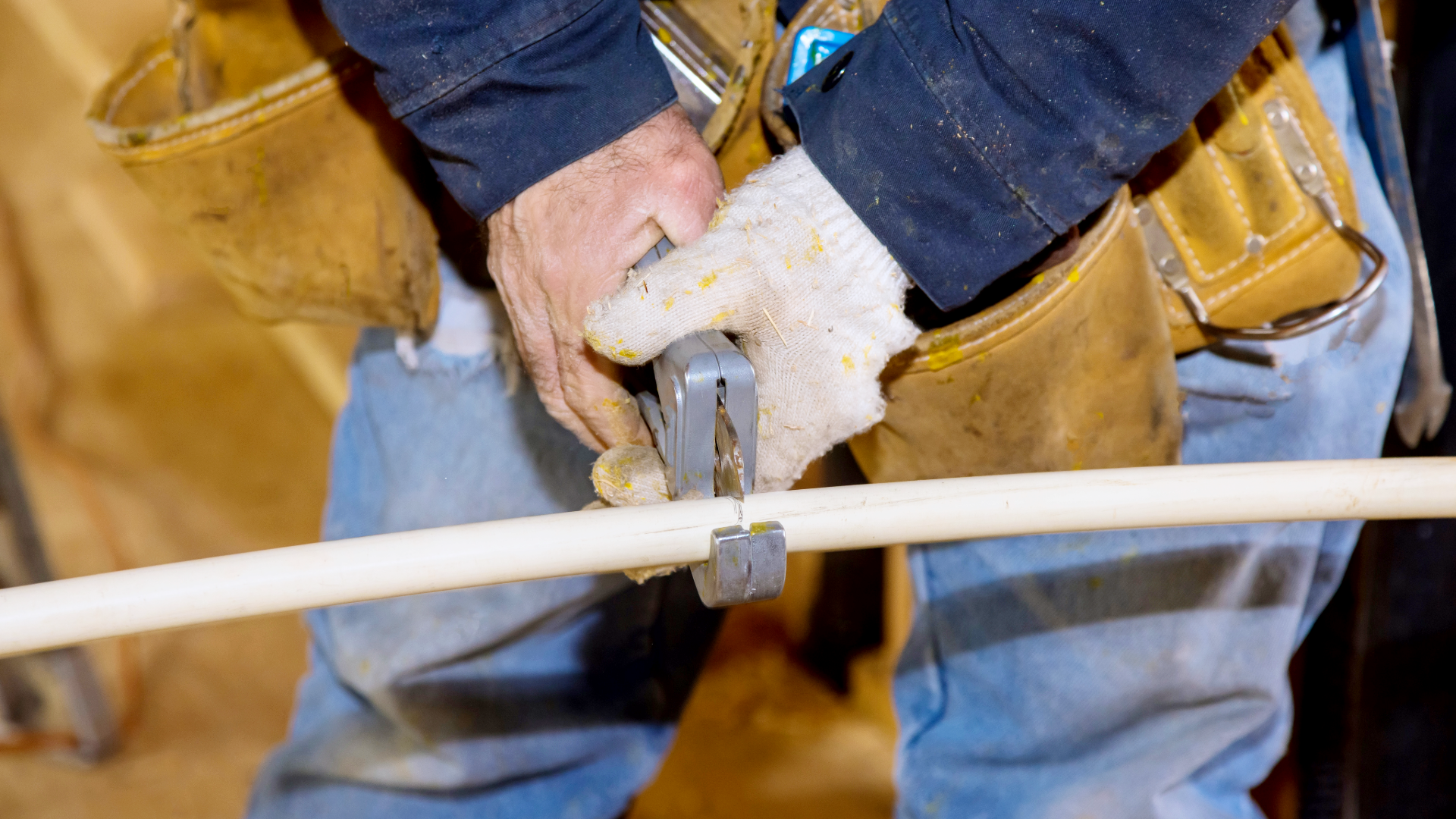


Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping the Primer: Failing to use primer can result in weak bonds between pipe and fittings that can lead to leaks or system failures over time.
- Cutting the Pipe Incorrectly: Uneven or jagged cuts can create poor fits and affect the seal. Always use proper tools and achieve precise cuts.
- Using the Wrong Solvent Cement: Not all cements are created equal. Ensure you’re using one designed specifically for CPVC piping to avoid compatibility issues.
- Rushing the Cure Time: Applying pressure or testing before the solvent cement has fully cured can weaken connections and lead to leaks.
- Forgetting Alignment Marks: Poorly aligned components can disrupt the flow of the system. Take the time to mark pipe and fitting positions during the dry-fit stage.
By following these tips and avoiding common mistakes, you can establish a secure and easy CPVC pipe installation.


Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Basic Maintenance Practices
Proper maintenance is key to the longevity and performance of any piping system, with CPVC no exception. By including simple routine checks into your schedule, you can prevent minor issues from turning into major problems.
Regularly check for leaks and cracks, especially at joints, connections, and segments where stress is most likely to occur. Pay particular attention to areas exposed to temperature changes or physical strain, such as turns, bends, valves, and equipment connections, as these are more susceptible to wear and tear. Small leaks or hairline cracks can escalate quickly, so address them early.
Ideal practice is to perform periodic inspections of the entire CPVC system. Look for signs of discoloration, warping, or other physical changes that might indicate an underlying issue, such as chemical exposure or prolonged UV radiation. Even in indoor applications, environmental factors can affect the integrity of a pipeline over time. Conducting an inspection every six months or more frequently in hard working systems can make a significant difference in maintaining an error free operating system
Repair Techniques for CPVC Systems
Despite its durability, CPVC pipelines may occasionally require repair due to damage or wear. Knowing how to identify and fix issues promptly will keep the system functioning smoothly with limited downtime.
Identifying and Repairing Damaged Sections
When you observe a leak or damage, start by isolating the affected portion of the system. Shut off the liquid supply to reduce pressure or allow drainage if possible. True union valves are engineered to make this process easier. Once isolated, carefully inspect the area to determine the extent of the damage. Small cracks might only require a patch or coupler, while severely damaged sections will need to be cut out and replaced.
Safety Measures During Repairs
Always be safe during any repair process. Wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and safety goggles, when handling solvent cement and primer. These materials contain chemicals that can cause irritation if they come into contact with your skin or eyes. Work in a well ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes, and keep all materials away from heat sources or open flames.
If you are unfamiliar with CPVC repair techniques or encounter complex issues, consider consulting a professional plumber or licensed contractor. Attempting repairs without proper knowledge can inadvertently worsen the problem or compromise the system.
Extending the Lifespan of CPVC Piping
With the right care and preventive measures, CPVC piping systems can last 50 years or more. Here are a few tips to maximize the lifespan of your CPVC pipelines:
- Prevent Over Tightening: Avoid over tightening threaded fittings during installation or maintenance. Excessive force can crack CPVC components or damage threads. Use hand tightening followed by a quarter turn with a wrench for a secure fit without the risk of damage.
- Monitor Water Temperature: Stay within the recommended temperature range for CPVC pipes, typically up to 200°F. Exceeding these limits can weaken the material and lead to plumbing issues.
- Protect Against UV Exposure: For outdoor installations, shield CPVC pipes from prolonged sun exposure by using UV rated insulation or painting them with a light colored, plastic approved paint. Ultraviolet rays can degrade the surface of plastic pipe and compromise its durability. Most professional quality CPVC pipes include UV stabilizers for sunlight protection. For more on this, see our resource on PVC and CPVC Sunlight Resistance.
- Use Approved Chemicals: Only use chemicals, solvents, and solutions specifically compatible with CPVC. Unapproved chemicals can interact negatively with the material, potentially leading to stress cracking, swelling, or breakdown. For more on this, see our CPVC Chemical Compatibility Guide.
- Flush the System Periodically: Over time, plumbing systems can accumulate sediment or other build-up that may reduce flow rates. Flushing the CPVC pipeline regularly can help prevent these issues and maintain optimal performance.
Comparing CPVC with Other Piping Materials
CPVC vs. PVC
At first glance, CPVC and PVC may seem similar. Both materials belong to the same family of chlorinated thermoplastics. However, there is a distinct difference in their molecular structure that makes them best suited for different applications.
Key Differences in Composition and Applications
The primary distinction between CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) comes from the chlorination process. CPVC is essentially PVC that has undergone additional chlorination, which strengthens its chemical resistance and allows it to withstand higher temperatures. Because of this, CPVC pipes are commonly used for hot water systems and applications involving corrosive chemicals.
PVC, on the other hand, is suited primarily for cold water applications such as outdoor irrigation, drainage systems, water supply lines, and certain industrial setups with lower fluid temperatures. PVC pipe is not designed to handle extreme heat and prolonged exposure to temperatures above 140°F as this can cause PVC to soften or connections to collapse.
Pros and Cons of Each Material
Pros of CPVC
- Handles hot and cold liquid applications effectively.
- Chemically resistant to many acids, bases, salts, inorganics, and select organics, making it ideal for chemical processing plants and industrial settings.
- Long lasting and corrosion resistant, even under harsh conditions involving reactive substances or elevated temperatures.
- Well suited for fume scrubbers and industrial ventilation systems due to its ability to withstand corrosive fumes and temperatures without degrading.
- NSF certified for potable water that ensures safe use in residential and commercial plumbing systems.
Cons of CPVC
- Generally higher cost than PVC, which can increase upfront project expenses.
- May require additional protective measures, such as UV resistant coatings, for prolonged outdoor use to prevent material degradation.
- Installation may require professional expertise in high performance applications and complex systems, adding to labor costs.
Pros of PVC
- Highly cost effective, making it an excellent choice for large scale projects with tight budgets.
- Lightweight and easy to handle, simplifying transportation and installation for contractors and DIY hobbyists alike.
- An excellent choice for ventilation systems and fume exhausts in mild corrosive environments, offering reliable performance at a fraction of the cost of other materials.
- Suitable for irrigation, drainage, and sewage systems due to resistance against regular water exposure.
- Readily available in a variety of grades and sizes to meet different project requirements.
Cons of PVC
- Not suitable for high temperature applications above 140°F.
- Limited chemical resistance compared to CPVC, making it less suitable for reactive or corrosive substances.
- Typically requires extra measures, such as insulation or UV resistant paint, for outdoor installations to prevent material damage.
- Understanding these differences is essential for choosing the right material. While PVC is best for limited temperature applications, CPVC offers the performance profile needed for more demanding projects, particularly those involving heated or corrosive media.
CPVC vs. Copper and PEX
When considering piping materials, CPVC often competes with traditional copper and modern PEX (Cross Linked Polyethylene). Each material has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice often comes down to cost, durability, and performance under specific conditions.
Cost, Durability, and Performance Comparisons
Cost
- CPVC is a more affordable option than copper, both in terms of material price and installation costs. Copper is not only expensive but requires skilled labor and tools for soldering.
- Compared to PEX, CPVC falls somewhere in the middle. While PEX can be slightly less expensive, the difference is often negligible, and CPVC remains a cost effective solution for both residential and industrial projects.
Performance
- Copper excels in high pressure and outdoor applications due to its metallic structure but can lose efficiency in hot water systems due to higher thermal conductivity that results in energy loss.
- PEX is valued for its flexibility and ease of installation, but it can’t handle harsh chemicals as well as CPVC.
- CPVC delivers reliable performance across a wide temperature, pressure, and chemical range, making it a versatile choice for complex plumbing systems.
Durability
- Copper is highly durable and resistant to UV exposure, making it suitable for outdoor and pressurized systems. However, it’s susceptible to corrosion in areas with acidic water or high mineral content.
- PEX, like CPVC, is corrosion resistant and also flexible, making it ideal for tight spaces. However, it doesn’t perform well in direct sunlight without protection and is more easily punctured by sharp objects.
- CPVC combines physical durability with chemical and corrosion resistance, outperforming copper and PEX in environments involving aggressive chemicals and heated liquids.
Points Influencing Material Choice
When deciding between CPVC, copper, and PEX, several points should be considered:
- Budget: If cost is a primary concern, CPVC or PEX are more economical than copper, especially for larger projects where material costs add up.
- Application Type: For applications involving high temperature water or chemicals, CPVC is often the best choice due to its superior resistance and thermal stability.
- Environmental Conditions: Outdoor systems may benefit from copper’s natural resistance to UV rays, PEX might be better suited for indoor plumbing, while CPVC has UV stabilizing compounds added during manufacturing that makes it suitable for indoor or outdoor installation.
- Ease of Installation: PEX is by far the easiest to install due to its flexibility. CPVC comes in second with its straightforward solvent welding process, while copper requires specialized skills.
Frequently Asked Questions about CPVC Pipe
Yes, CPVC pipes can be used outdoors as professional grade CPVC pipes are specially engineered with UV stabilizers like titanium dioxide and carbon black to resist UV damage, surface degradation, and discoloration. This advanced design ensures durability and reliability for outdoor applications such as irrigation, plumbing, or industrial fluid transport without requiring additional protective measures like paint. While CPVC pipes are built to withstand environmental exposure, periodic maintenance and extra shielding in high exposure areas can work to further extend their lifespan
Yes, CPVC is certified for potable water use and meets NSF (National Sanitation Foundation) standards. This certification ensures that CPVC does not contain and will not leach harmful chemicals into the water, making it a safe and reliable choice for transporting drinking water in residential, commercial, and industrial systems. Its resistance to corrosion and scaling further improves water safety and quality.
The key difference lies in the chlorination process. CPVC undergoes additional chlorination, which improves its chemical resistance and ability to handle higher temperatures. While standard PVC is best suited for cold water and drainage applications, CPVC excels in hot water systems and environments involving corrosive chemicals.
CPVC pipes have an impressive lifespan, often exceeding 50 years when installed and maintained properly. Their resistance to corrosion, chemical damage, and scaling minimizes wear over time, giving CPVC a high return on investment and making it a durable choice for a wide range of applications.
Yes, CPVC is known for its straightforward installation process. It’s lightweight and can be cut and joined using basic tools. The solvent welding method makes connecting pipes and fittings quick and secure, which reduces labor time and complexity compared to materials like copper or steel.
CPVC is designed to withstand temperatures up to 200°F, making it suitable for heated liquid systems and industrial processes. However, it’s important to stay within recommended temperature ranges to maintain the pipe’s performance and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions about CPVC Pipe
Can CPVC be used outdoors?
Yes, CPVC pipes can be used outdoors as professional grade CPVC pipes are specially engineered with UV stabilizers like titanium dioxide and carbon black to resist UV damage, surface degradation, and discoloration. This advanced design ensures durability and reliability for outdoor applications such as irrigation, plumbing, or industrial fluid transport without requiring additional protective measures like paint. While CPVC pipes are built to withstand environmental exposure, periodic maintenance and extra shielding in high exposure areas can work to further extend their lifespan
Is CPVC safe for drinking water?
Yes, CPVC is certified for potable water use and meets NSF (National Sanitation Foundation) standards. This certification ensures that CPVC does not contain and will not leach harmful chemicals into the water, making it a safe and reliable choice for transporting drinking water in residential, commercial, and industrial systems. Its resistance to corrosion and scaling further improves water safety and quality.
What makes CPVC different from standard PVC?
The key difference lies in the chlorination process. CPVC undergoes additional chlorination, which improves its chemical resistance and ability to handle higher temperatures. While standard PVC is best suited for cold water and drainage applications, CPVC excels in hot water systems and environments involving corrosive chemicals.
How long does CPVC piping last?
CPVC pipes have an impressive lifespan, often exceeding 50 years when installed and maintained properly. Their resistance to corrosion, chemical damage, and scaling minimizes wear over time, giving CPVC a high return on investment and making it a durable choice for a wide range of applications.
Is CPVC easy to install?
Yes, CPVC is known for its straightforward installation process. It’s lightweight and can be cut and joined using basic tools. The solvent welding method makes connecting pipes and fittings quick and secure, which reduces labor time and complexity compared to materials like copper or steel.
Can CPVC handle extreme temperatures?
CPVC is designed to withstand temperatures up to 200°F, making it suitable for heated liquid systems and industrial processes. However, it’s important to stay within recommended temperature ranges to maintain the pipe’s performance and longevity.
Takeaway
Whether you're upgrading a home plumbing system or installing pipes in a commercial or industrial setting, CPVC offers a winning combination of performance, durability, and cost effectiveness. To explore top quality CPVC solutions, shop our extensive inventory of CPVC pipes, ductwork, fittings, and pipe accessories and find everything you need for your next project. Shop now and see why CPVC is the trusted choice for professionals and homeowners alike.